OVERVIEW
Patients with diabetes need to get their eyes checked regularly. With India becoming the diabetic capital of the world, managing complications related to diabetes is a major concern. One of the complications is diabetic retinopathy, which is fast gaining importance as a cause of visual impairment among a large population of individuals. If left untreated, it can get worse and cause some loss of vision, or blindness in severe cases.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition that leads to inadequate control of blood sugar (glucose). In normal persons, blood sugar is tightly regulated by a hormone secreted by the pancreas called insulin. Diabetes mellitus (also called just diabetes) occurs when the level of sugar in blood becomes higher than normal. There are two major types of diabetes :
- Type 1 diabetes that occurs due to a condition that leads to lack of insulin production in the body. This usually begins in children or adolescents or in young adults.
- Type 2 diabetes that occurs due to relative deficiency of insulin in the body. This type of diabetes is common among the obese and overweight and is usually seen in the middle aged.
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Retinopathy or retinal disease encompasses a variety of pathologies that affect the retina. These can affect vision significantly. In most cases retinopathy is caused due to the damage to the tiny blood vessels in the retina.
Retinopathy can be caused by diabetes and high blood pressure. Diabetes may also cause other eye changes and damages including cataracts and glaucoma.
As the blood sugar remains high and uncontrolled among diabetics over several years, the tiny blood vessels in the retina are damaged. In addition the small nerves that take away information from the retinal cells are also damaged due to lack of adequate blood supply to them.
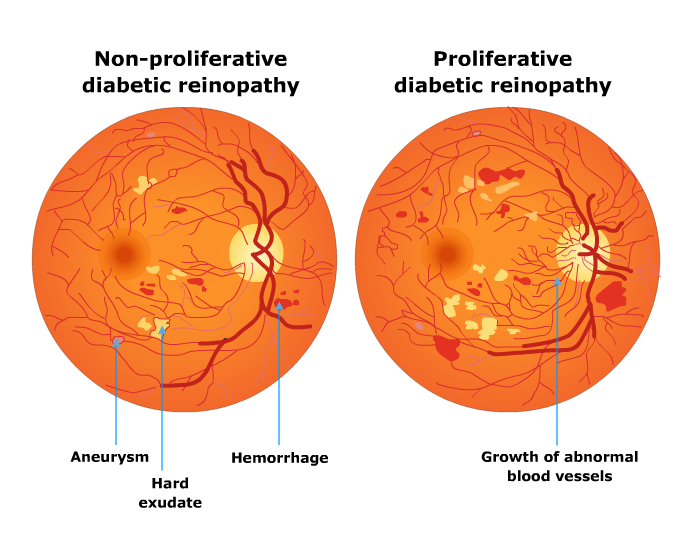
Symptoms
Early diabetic retinopathy seldom causes any symptoms. As the condition progresses there may loss of vision. Over time the condition worsens and leads to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in people of the working age group worldwide especially in developing and developed nations.
Some of the symptoms include –
Risks of diabetic retinopathy
Retinopathy is one of the more common complications of diabetes. Several factors raise the risk of getting diabetic retinopathy. Some of these include –
Prevention of diabetic retinopathy –
Diabetic retinopathy can be prevented if the blood sugar is well controlled. Blood glucose is controlled by adopting a healthy and balanced diet along with physical activity and medications to lower blood sugar. Apart from blood sugar, blood pressure and blood cholesterol also needs to be tightly controlled. Weight loss and cessation of smoking are important preventive measures.
All diabetics should get their eyes checked routinely (annually) to detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy. Treatment can prevent loss of vision and blindness in most cases.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by testing vision and taking digital photographs of the retina. For eye examination drops are put in the eyes to make the pupil as wide as possible. Thereafter instruments are used to look at the retina and take its picture. For retinopathy and the blood vessels a fluorescein angiogram is conducted. A special dye is injected into one of the veins in the arm. This dye then travels to the blood vessels in the eye. When examined with a special camera, the blood vessels light up to reveal abnormalities.
Treatment
Treatment of retinopathy is usually given by laser therapy. Laser treatment is helpful in presence of abnormal blood vessels in the eye. A laser light is focused on the retina to make tiny burns. These help seal the leaks from blood vessels, and stop new vessels from growing further. Several hundred burns may be needed to treat retinopathy. This is also called photocoagulation. Photocoagulation is not usually a painful procedure but may cause some pricking sensation. Laser therapy usually prevents diabetic retinopathy from getting worse. However, laser treatment cannot restore vision that is already lost.